Public transit in India has a problem of plenty, on multiple levels. Plenty of obstacles, that is.
Obstacles, such as lack of political will to plan and execute projects at the state level, the Not-In-My-Backyard (NIMBY) syndrome among persons who may or may not be affected by a planned project, a militant civil society, among various others.
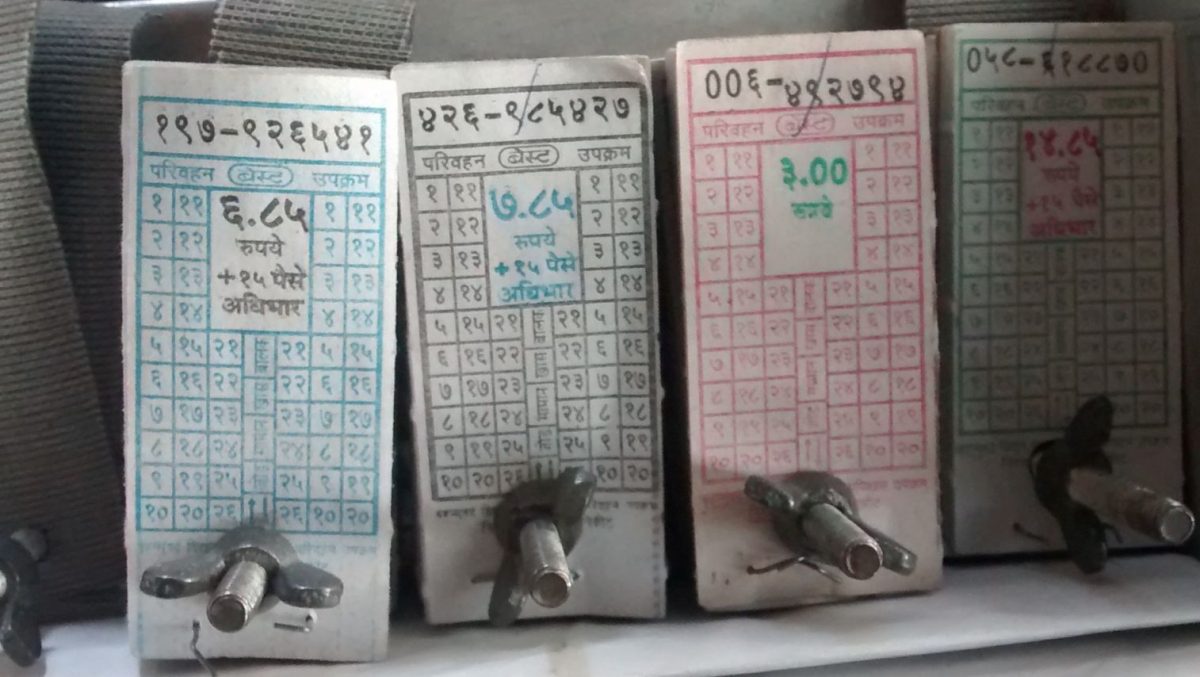
One of these obstacles also include the variety of fare collection media. Most cities of India have not been able to replicate successful projects, like Oyster (London), Octopus (Hong Kong), Nol (Dubai), OMNY (New York), on their public transit systems, demonstrating a lack of coordination between the different public transit system operators. Most of such attempts – such as the GO MUMBAI card, designed for a single ticketing system on the BEST and the Mumbai Local – failed miserably, due to the transit operators’ resistance, or a half-baked product, or a private contractor lacking the required expertise to support the project, etc, or a mix of all of them[1]. Although, to be fair, the public transit systems in cities like London, Hong Kong, Dubai, New York etc are run directly or indirectly by a unified city-level transit agency, like Transport for London, Metropolitan Transportation Authority (New York), Roads and Transport Authority (Dubai) and MTR Corporation (Hong Kong) – something which, as conventional wisdom suggests, may be in the realm of impossibility in India.
A national common mobility card had been on the drawing board since 2010. The card was titled “More” – a reference to the peacock – and was first launched in Delhi, for unified payments on the Delhi Metro and DTC buses. This too, failed, due to a lack of effort from all stakeholders. Delhi Metro, DTC and the Rapid Metro Gurgaon now have the ONE DELHI card, a closed-loop system.
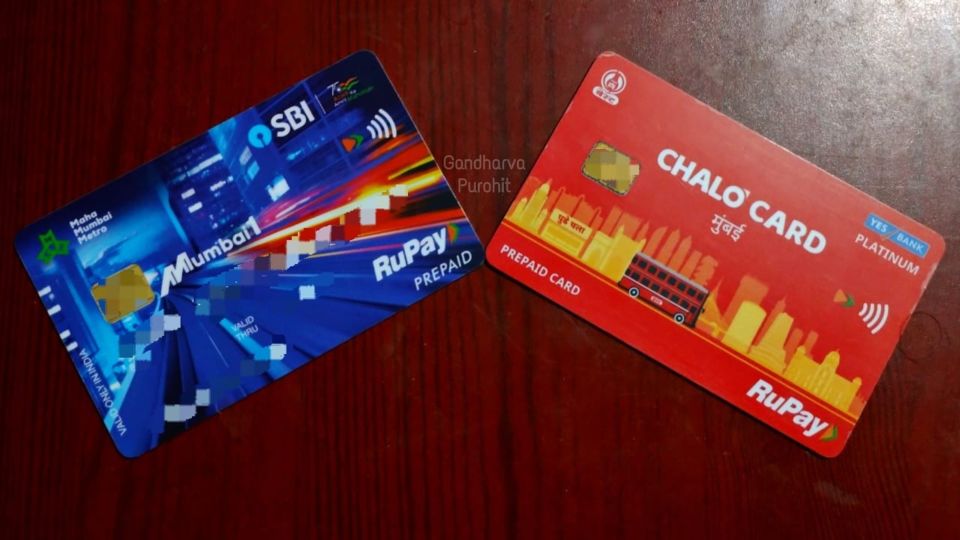
In view of the failures of the past on this front, the Modi government launched the National Common Mobility Card in 2019, with a different approach this time. This time, banks too were involved in the project, and so was the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI)[2]. Under this new approach, NCMC wasn’t launched as one card, but as a set of technological standards developed by Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL), the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC), and the NPCI, to be adopted by all transit operators and projects, who are free to choose their own issuer and acquirer banks to run their respective fare collection and management projects. NCMCs mandatorily have to be RuPay contactless cards issued by banks – debit, credit or prepaid – making them eligible to be used for purposes other than public transit fares too.[3] Due to them being RuPay cards issued by banks, it is easy to scale up operations for public transit systems not using automated fare collection (AFC) systems, such as buses.
While now is the closest India has ever come to a truly “national” common mobility card, there is still a long way to go. Cities like Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, continue to be very heavily reliant on suburban railway services operated by the concerned zones of the Indian Railways, by using legacy infrastructure. Most importantly, suburban railways, like the mainline long-distance operations, use the proof-of-payment system (PoP) for fare collection. The PoP system entails passengers buying tickets from the ticket windows or online (through the UTS app), and then using the train. The only fare control system, in this case, are random checks by ticket examining staff onboard or at the destination. Most of the times, these random checks are limited to AC trains, and the first-class carriages on non-AC trains. Thus, this makes for a highly inefficient mode of fare collection, control and management, due to the high possibility of fare evasion by passengers.
However, there seems to be no viable alternative to PoP systems on suburban railways. While suburban rail systems currently under construction, such as K-RIDE’s Bengaluru Suburban Rail Project, can adopt the AFC systems, changing the fare collection system on existing systems, and that too, heavily-used systems like the Mumbai Suburban Railway, may prove to be difficult without rebuilding the system from the ground up. Moreover, due to there being different fare classes and products (single journey tickets, return journey tickets, season tickets for first and second class, and also the luggage compartment), converting to AFC systems is all the more difficult.
[1] R. Aklekar, Mumbai’s experiment with smart card fails, DNA (04/01/2010), available at https://www.dnaindia.com/speak-up/report-mumbai-s-experiment-with-smart-card-fails-1447695, last seen on 26/01/2023.
[2] https://www.npci.org.in/PDF/npci/rupay/2020/Concept_Note_Implementation_of_RuPay_qSPARC_based_NCMC%20v2.1.pdf
[3] https://www.npci.org.in/what-we-do/rupay-contactless/live-members
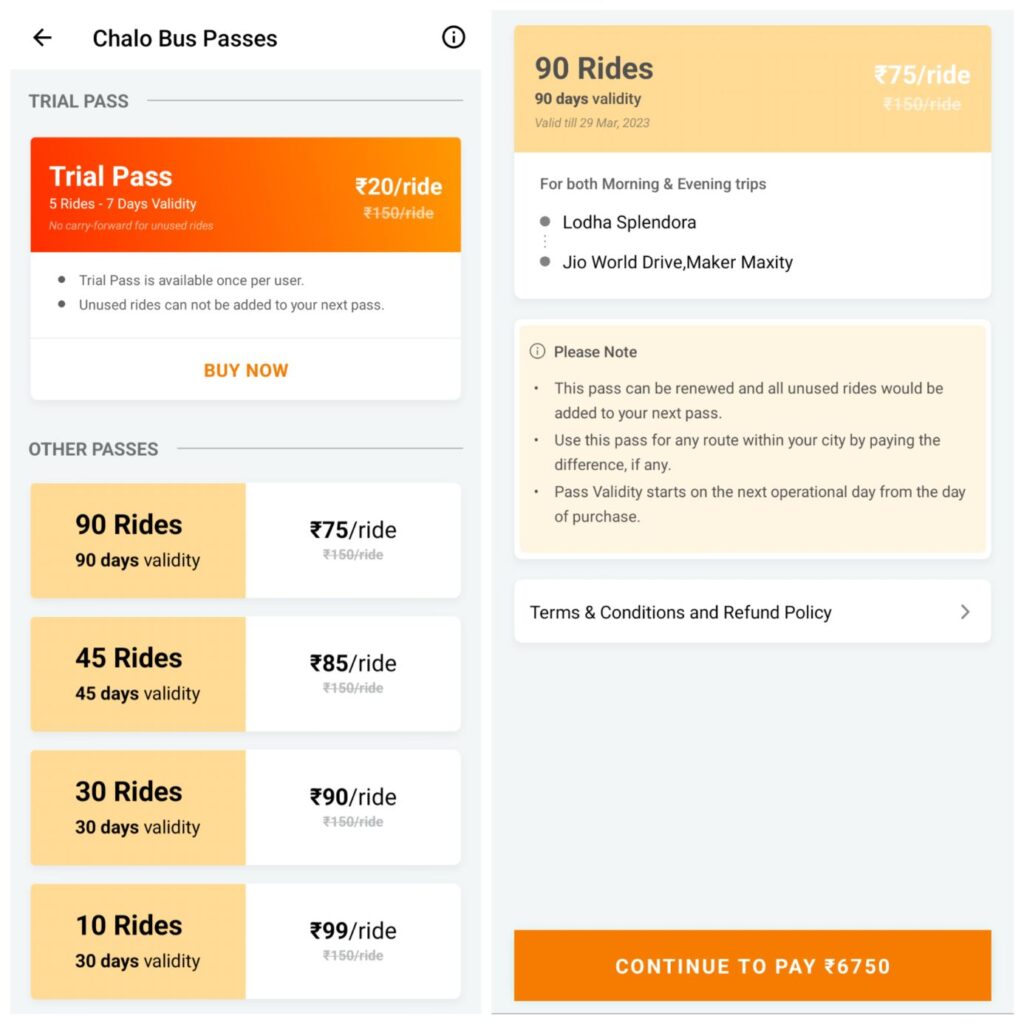
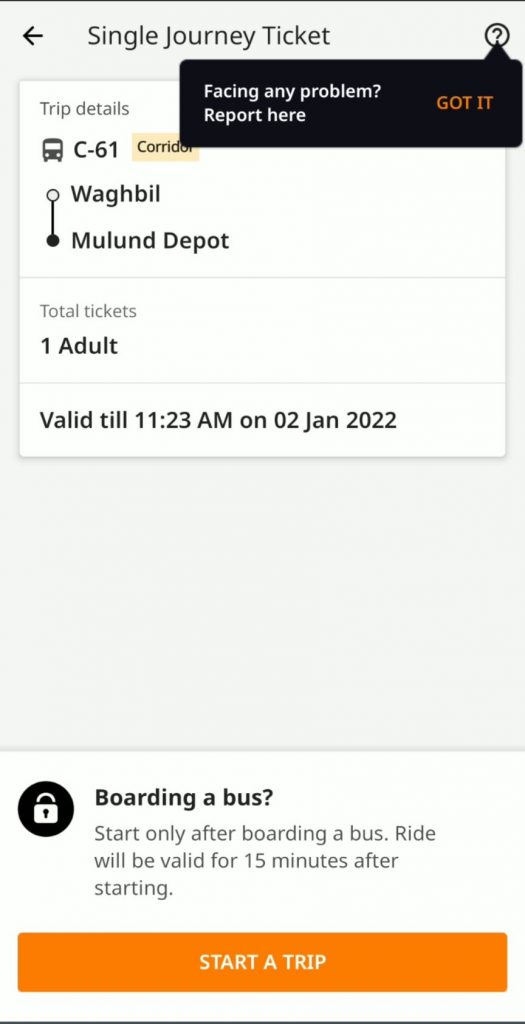
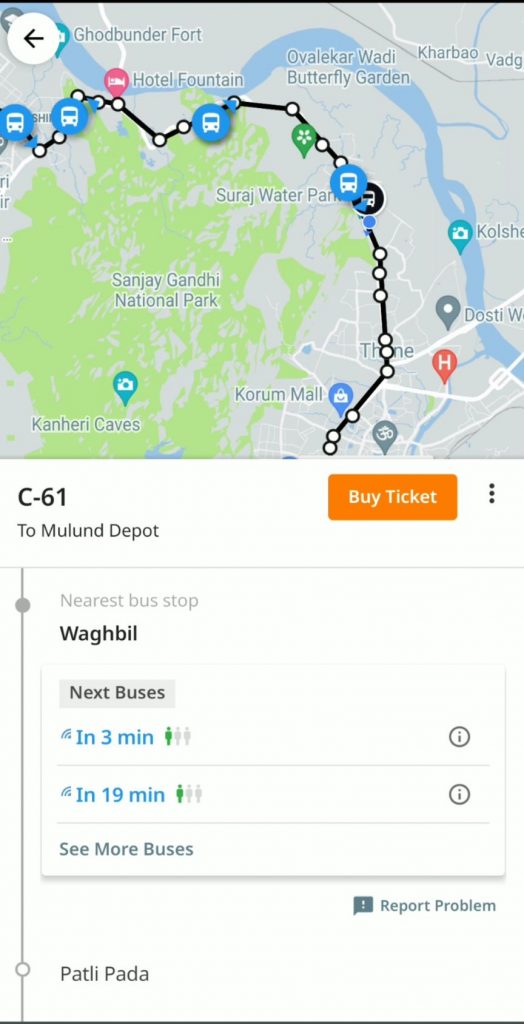
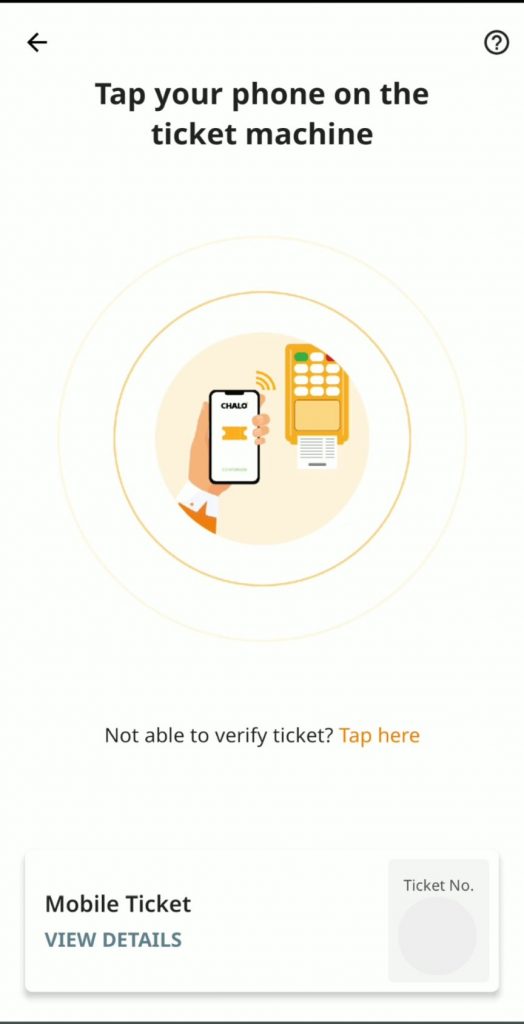
Featured Image: Mumbai One and Chalo NCMC (Photo: Gandharva Purohit, Used with Permission)
Also Read: American Elections Are Like Indian Transport: Fragmented
![]()