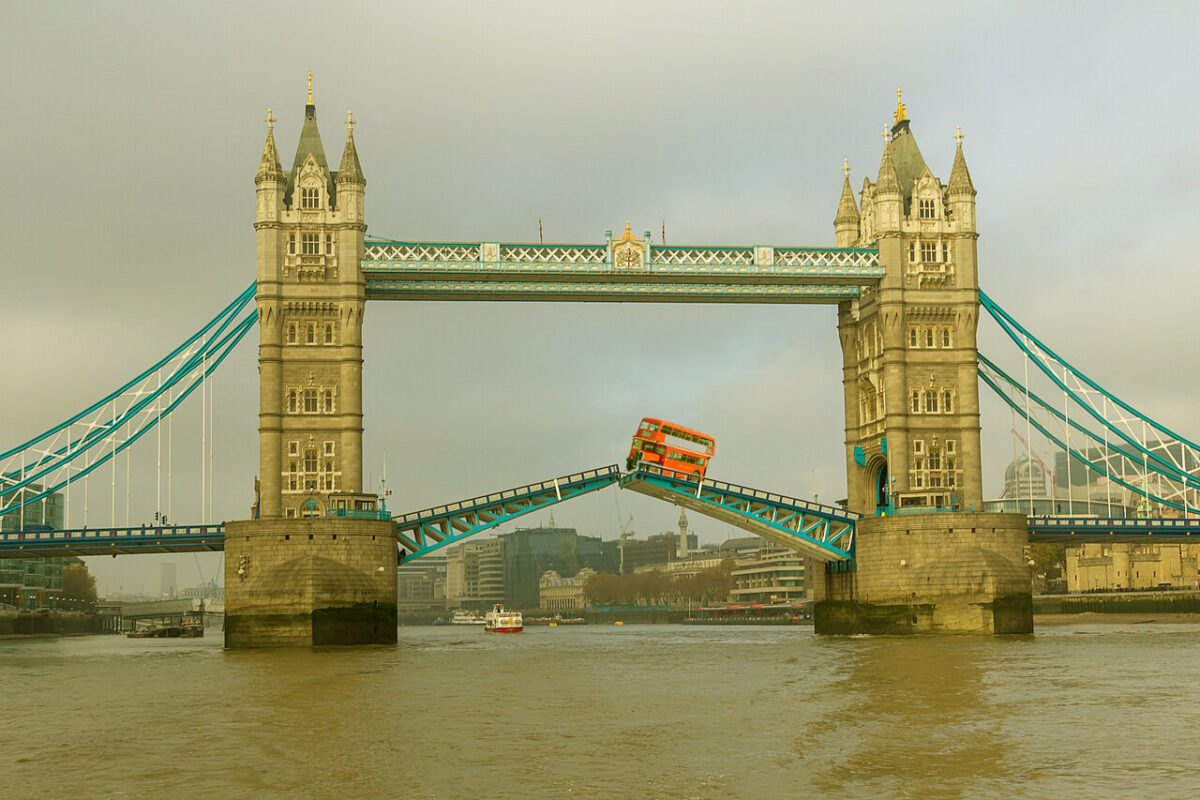
We’ve seen buses do interesting things. We’ve seen double-decker buses do interesting things as well. But what if I told you about the time that a double-decker bus jumped a drawbridge that was opening up?
It was 30 December 1952. Albert Edward Gunter was driving an AEC Regent III RT double decker bus on Route 78 across the Tower Bridge (not to be confused with the nearby London Bridge, made popular by the rhyme London Bridge is falling down) towards Shoreditch. Back then, when the bridge was to be lifted, a gateman would ring a warning bell, clear the bridge, and then the watchman would raise the bridge. However, on that day, a relief watchman was on duty and things didn’t go as expected. Gunter had already begun driving across the bridge, and was nearly at the edge of the South Bascule as it began to rise.
Realising the trouble he was already in, Gunter floored the accelerator to hit around 19 km/hr and jumped across. Luckily, the North Bascule was yet to go up and Gunter and all 20 of his passengers landed safely on the other side with Gunter being the only injured – he broke his leg. Interestingly, the bus was intact too.
For his act of bravery and quick thinking, Gunter was given a £10 reward and a day off. When asked how he would spend his reward money, his response was, “Five for me, and five for the missus”, referring to his wife. Later, Gunter apparently said “I’d always wanted to jump the bus over the gap! And I got a day off and a tenner for it, to boot!”
According to the Tower Bridge section of City Bridge Foundation (Bridge House Estates), the incident has since become a part of London’s culture and many pop-culture references have been made.
The 1997 musical comedy Spice World starring the British pop girl band Spice Girls had a scene where Victoria “Posh Spice” Adams (Victoria Beckham) drove a bus decorated in the Union Jack across the bridge with the bascules lifted. Of course, it was filmed with a scale model. The British preschool animated series Peppa Pig had an episode titled Peppa Goes To London where the Queen (Elizabeth II) gives Peppa a bus tour and being impatient drives across the open bridge. The incident was also the inspiration for the children’s book The Tower Bridge Cat featuring a cat named Bella and a bus driving off the bridge. Cats and buses, two of my favourite topics, seems fun, eh? You can learn more about the award-winning book and its sequels here.

Tower Bridge in fact even has an educational tour of the incident for school children, completed with a costumed storytelling session.
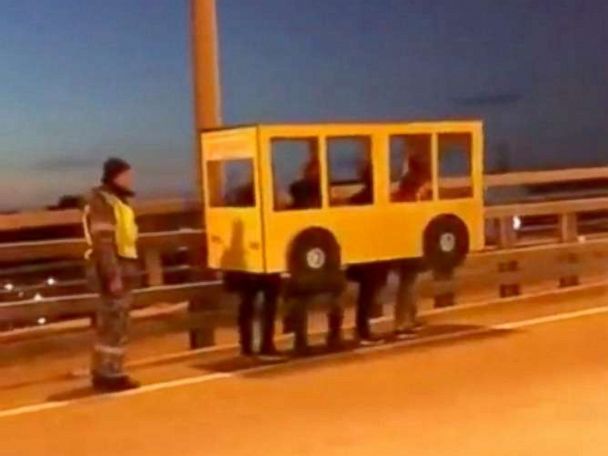
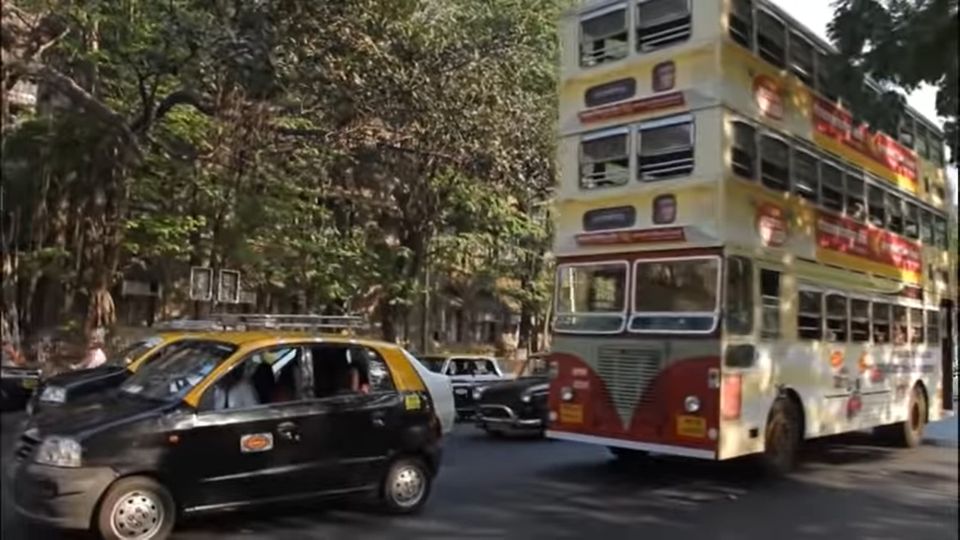
Buses can be a fun topic. Remember, when the Russians dressed up as a bus or when racing Double Decker buses was a televised sport?
Featured image: Reconstruction of a the AEC Regent III RT on the Tower Bridge (Image created by Samuel Sathiyanathan for BESTpedia)
![]()