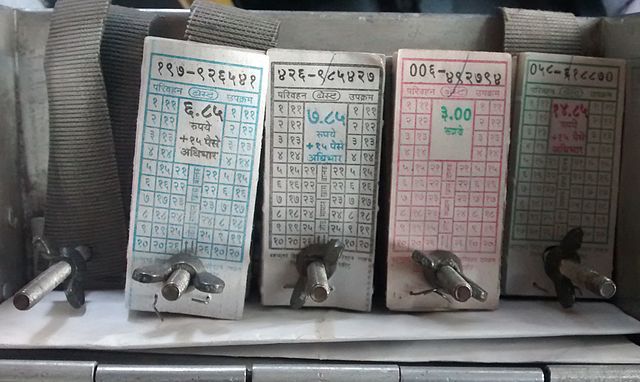
Daily Passes are something that drives every Transco today. It is not only beneficial for the transport body, but also for the commuter. A Daily Pass allows a commuter to travel unlimited for the day it has been issued at a nominal cost. In the long run, it is very useful. Some cities, like Bombay, and Bangalore, have special Daily passes for regular buses and AC buses. Now, there is a lot more to Daily Passes than what is visible on the pass itself.
The biggest headache for a transco is the resale/reuse of passes. To prevent this, several of them implemented select measures. Now, let us have a look at some of these measures.
PMPML

PMPML has had Daily passes right from the PMT-PCMT era. Even back then, it had mandated a PMT/PCMT issued Identity Card for the Daily Pass. With the subsequent merger of the PMT and PCMT into the PMPML, the PMPML started issuing the ID cards and Daily Passes. The old PMT era Daily Pass is today used as a PMPML Weekly Pass with the start and end dates punched out.
The PMPML Daily Pass, is a Pink or Off-white coloured ticket, with space for the date, month and last three digits of the ID card printed on it. This is valid on all buses including the Rainbow BRTS, Katraj-Swargate-Hadapsar BRT Volvo buses, but are not valid on the AC Pune Darshan and CityAir Airport connectivity buses. The pass is valid on the entire operational region of PMPML, outside the municipal limits of both Municipal Corporations. To prevent its resale, the ID card number is punched out. The pass cannot be used on the same date a year later because the ID card would no longer be valid by then.
MTC and TNSTC

MTC and TNSTC have both had Daily passes in large cities including Chennai and Coimbatore for a long time. In Coimbatore, these passes require a local ID proof in order to be purchased and are valid only if the holder shows the ID card as well. In Chennai, known as the Travel As You Please ticket, they require an MTC ID card for Weekly/Monthly passes which costs ₹5 [according to the website, while I paid ₹20 for it]. The pass costs ₹50 per day and is not valid for night services. There is no Daily/Weekly/Monthly Pass for Volvo buses, which is surprising.
BMTC and KSRTC

BMTC is undoubtedly the leader when it comes to Daily Passes. It has a wide variety of Daily Passes, something like their wide variety of buses as well. They currently have three major daily passes for people who do not have any other pass. This includes a regular daily pass for non-AC services that comes in two forms: One for those who own a BMTC ID Card, and one that costs ₹5 more for those who don’t have a BMTC pass. Those who purchase the former have to write their ID number on the pass, and all passholders have to sign the pass. The Vajra Gold Day Pass costs twice, and is valid on all buses except the Daily Rounds, and Vayu Vajra buses. A pass that is priced between the two exists for AC-Suvarna/Tata Marcopolo AC buses. ID Cards are of two types: One is the Loyalty Card that costs ₹25 for a year and is valid ONLY with the non AC Daily Pass, while the ₹100 ID Card is mandatory for a Monthly Pass as well. Today, BMTC conductors only sell the Gold Day Pass if the commuter has a valid Government issued ID or BMTC ID. Due to high sale volumes, BMTC changes its pass everyday. Each day of the week has a different, colour-coded pass with the day of the week written in Kannada/English and the serial number of the pass starting with a different series for different days of the week. BMTC also has a Saral and Sarag pass that it issues with the BMRCL. Saral is a Gold Daily Pass that allows unlimited travel on the Namma Metro, while Sarag is the same for non-AC services. All Daily Passes are valid throughout the operational area of BMTC. In 2009, BMTC and KSRTC had jointly released a ₹70 rupee pass that was valid on all non-AC BMTC as well as non-AC KSRTC Karnataka Sarige busees in the nearby districts. The AC pass now costs ₹150 including a 6% Luxury Tax introduced by the Central Government.

KSRTC in the Mysore City Transport Department has a similar arrangement. It has two passes, one for AC buses that costs ₹96 [with the Service Tax] and one for non AC buses that costs ₹50. The pass is valid throughout the service region of the MCTD and is valid on all MCTD buses. Compared the Bangalore, both the pass rates as well as the fares are low.
TSRTC
![TSRTC Travel As You Like [TAYL] Ticket.](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fa/TSRTC-Hyd-AC-Daily-Pass.jpg/338px-TSRTC-Hyd-AC-Daily-Pass.jpg)
The Telangana State Road Transport Corporation has a Daily Pass System in Hyderabad, referred to as the Travel As You Like [TAYL] Ticket. It is printed using the ETM. It is of two variants, one priced at ₹70 for non-AC, regular, and Metro Express buses and the ₹150 pass which is valid on Sheetal and Metro Deluxe Volvo buses. The pass now costs ₹160 after a 6% Luxury Tax introduced by the Central Government. The conductor asks for the passengers age and mobile number, both of which are printed on the ticket. The passenger is required to write their name as well as sign the pass. The pass is valid in the Twin city regions of Hyderabad and Secunderabad.
In June 2016, TSRTC announced that Daily Passes would be valid 24 hours from the time of issue. Later on, they announced that the passes could be purchased upto 7 days in advance.
BEST

The story with BEST is a different one altogether, atleast today. A few years ago, BEST had daily passes similar to the current PMPML passes except there was no ID card. There were two types of Daily Passes, the Regular and Limited Pass for ₹25, which as the name suggests was valid on regular and Limited Routes, and the Corridor Pass at ₹40 which was valid on Express and Corridor services. The pass was punched with the date and gender, and to prevent misuse, the conductor would scribble a description of purchaser on the back. However, later on BEST began insisting on ID proof and asked commuters to write the ID number on the back of the pass. All this changed when BEST went digital in 2011-2012.
Once BEST went digital, they made it mandatory for commuters to have an RFID card for ALL passes. A horizontal ID card was issued for monthly and quarterly passes while a vertical one was issued for prepaid cards. Both can be used for Daily Passes. Till February 2015, BEST charged ₹50 for a non-AC Daily Pass and ₹150 for an AC pass. These passes are also referred to a Magic Daily Pass [AC and non-AC]. After February, BEST increased the rates to ₹70 and ₹200 respectively. All Daily Passes are valid throughout the operational area of BEST including Navi Mumbai, Thane, and Mira-Bhayander.
However, in September 2015, the BEST decided to introduce a new change in the non AC Magic Pass. As per the new system, the BEST now has three kinds of non-AC passes:
- The regular ₹70 Magic non-AC pass that is valid throughout BESTs operational limits including Navi Mumbai, Mira Bhayander and Thane.
- The ₹50 Suburban pass that is valid in the Suburban limits, and upto Mahim/Sion/Rani Laxmi Chowk in the South and Dahisar/Mulund Check Naka in the North.
- The ₹40 City pass that is valid in the Island city region, again upto Mahim/Sion/Rani Laxmi Chowk.
No daily pass on Sundays or Public Holidays requires an ID card. Anyone can buy a pass. Since it isn’t tied to an ID card any longer, it needs to be carefully preserved throughout the day, and the conductor must enter the right gender. Of course, if you give your ID card, it logs it onto your ID card, and automatically detects your gender and the conductor can still validate the card with the ETM.
The Magic AC pass remains the same, however, on Sundays, half the AC buses are cancelled, thus making the Magic AC pass pointless. I personally feel BEST should either charge less for the AC pass on Sundays or go the BMTC way and charge extra for non ID passes on all days. Any pass can be purchased on any bus because they are all digitally printed.
Also Read: A Trip Down Memory Lane: Pictures of BEST’s Punched Daily Passes
MSRTC
MSRTC has a 4 day, 7 day, Monthly, quarterly and annual pass called the Travel Wherever you Like Pass. They have been in operation since 1988. The current form of the pass is similar to BEST’s Daily Pass system. Users are required to have a Smart Card for it.
For pricing, two seasons have been created:
- Congested Season: 15 October to 14 June.
- Non Congested Season: 15 June to 14 October.
Pass rates vary per season. The cost of the passes is mentioned on the MSRTC website.
DTC

This is probably the first time I’m mentioning DTC on BESTpedia, but being one of the transcos catering to a large city in India, I guess this needs to be mentioned.
The DTC refers to its Daily Pass as a Green Card. The DTC Green Card is neither green, nor is it a card. There are two variants. ₹40 for non-AC and ₹50 for AC. Yes, you read that right. The Delhi AC Daily Pass is cheaper than Bangalore, Pune or Mumbai’s non-AC pass of ₹70! But then, it is hardly surprising, given that Delhi has been spoilt by subsidies solely by being the Capital of India. The Green Card is available with the conductor of the bus and a non-AC bus conductor sells both types. It looks like a regular ticket, and the conductor writes the commuters name and age on it, while marking the date and month. That’s it. No other measure to prevent resale. The downside to this is:
- Very few AC buses compared to regular ones.
- Due to it being so cheap, AC buses are as crowded as their non-AC counterparts.
- Neither pass is valid on the Orange-coloured Cluster services, which form roughly 1/3rd of the buses.
- This pass is ONLY valid within Delhi borders, and not in the rest of the NCR.
CTU
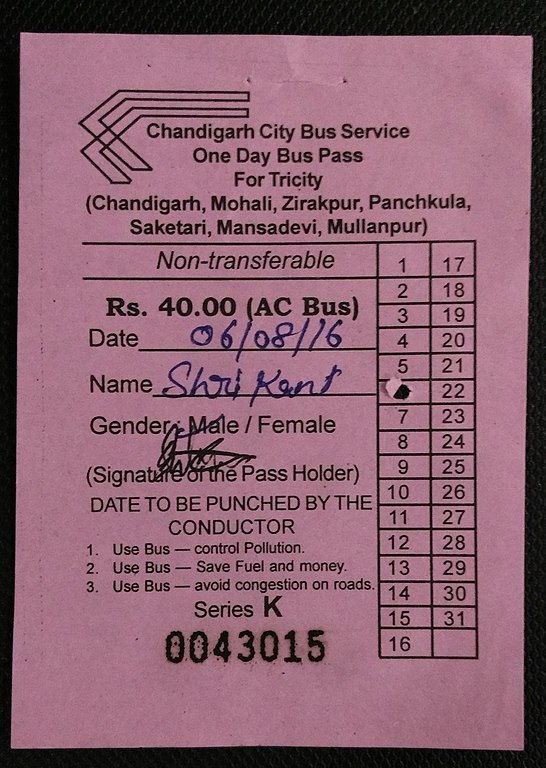
Another first on BESTpedia, this is the first time I’m mentioning the Chandigarh Transport Undertaking. The CTU, under the UT administration operates buses throughout the Tricity region comprising of Chandigarh, Panchkula and Mohali.
The CTU has two kinds of Daily Passes: A green coloured one for non-AC services that costs ₹30 and a pink coloured one for AC services, priced at ₹40.
Both passes are valid throughout the Municipal Limits of the Tricity Region comprising of Chandigarh, Mohali, Panchkula, Zirakpur, Saketari, Manasdevi, and Mullanpur. For routes that go beyond the Municipal borders, such as to Landran, the pass is valid only till Sohana, where the Municipal Corporation’s jurisdiction ends.
Similar to the DTC Green Card, only the Passenger’s name is written on the ticket. The date is both written, as well as punched by the conductor. Passes are available aboard a bus, or at the ISBTs.
So at the end of the day, we can conclude that BMTC is the undisputed leader of Daily Passes. BEST, lags a bit behind, but is great with technology. PMPML, is with BEST. DTC, on the other hand is a totally different ball game. While people may not realise it, Daily Passes are very crucial, for both the commuter as well as the transco. It is useful for tourists and business people.
Which Daily Pass is meant for you? Share on XHave you ever used a Daily Pass?
Do leave your feedback below.
![]()