BMTC’s much touted ITS is nothing but a fraud. There is a lot more to it, but if you happen to be an ardent BMTC fan, I’d suggest you read this post before defending this third rate transport corporation that needs a major revamp.
For starters, the ticket machines are the biggest problem right now. Some BMTC buses, both the regular rattletraps as well as the Volvo and Corona fleet use the older Ticketing Machines; The older Quantum Aeon machines and not the Verifone machines that Trimax has supplied. These machines are not compatible with the current system. As simple as that. As if this wasn’t enough, there are some Volvo buses where the conductor still uses the older manual ticketing system. He tears out a ticket from his bunch and gives it.
Now, coming to the crucial part:
I wanted to travel from Central Silk Board to Arekere Gate at 7.30pm. I pulled out my phone and checked the BMTC app. It showed me a 411GT Volvo with the number KA57F996 with an ETA of 12 mins. The map showed the bus at Iblur. I waited. I tracked the bus on the map. After Agara, he suddenly turned into HSR Layout, before coming out at 5th main. I had a doubt when I saw the bus with a 57F registration. After a few minutes I saw it whiz past me. A green Vayu Vajra on an ORRCA route.
I looked up the app again. It showed the next 411GT 11 minutes away. This time, the number was KA01FA1418.
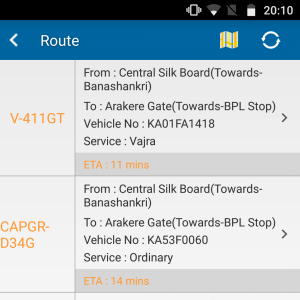
Along with this, the BMTC app shows me buses contracted to Manyata Tech Park, Bagmane Tech Park, ORRCA, etc. All the buses which a regular commuter cannot board.
Fine. I waited. I waited for 25 agonising minutes, possibly because of the traffic. Silk Board is not to blame here. It does its job well by holding up traffic so that the signals on the other side do not get overwhelmed.
The bus arrived alright, but just as I had expected, it turned out to be something else. A 500NA.

This annoyed me to no end. Here I am wasting 40 minutes of my time, and BMTC is taking me for a ride [figuratively].
Now, listing out buses leased out, itself is misleading. For someone new to Bangalore, they simply won’t know that this bus is not meant for them. Listing out a bus as en route, but not plying that route at all, is not only misleading, but fraudulent. I’d call it a criminal waste of my time if I could.
Now, the situation wouldn’t be so bad normally, but this is Bangalore, where the state government has made life difficult for commuters in every possible way. Starting with ridiculous laws for Uber and Ola, thanks to which it is near impossible to find a cab, even a sharing/pooled one. Next, the government came up with a plan to Nationalise bus transport in the state. While I’m not really fond of all those flashy, colourful Private buses on the road that drive like Delhi’s Blueline buses, they are the lifeline for some sections of the society, mainly those going from far flung suburbs to KR Market. On top of all this, remember what a chat with a conductor revealed?
I’d like to title this as the Great Bangalore Transport Scam. Sab Mile Hue Hain.
Remember that all the data from the ITS will be freely licenced for others to tap into the API and use it for their apps. Such wrong data is just going to screw things up badly.
I hope the BMTC learns something fast. It already has a snarky reputation for not stopping at bus stops and not opening its doors when it does stop.
What can be done here?
Decentralisation is pointless. Handing BMTC over to the BBMP is as good as the GoK handling it. Both are inept, incompetent, and brazenly corrupt.
BMTC's ITS is a sham. #TransitssuesIN Share on XWhat are your thoughts?
Note: We decided to give the ITS a second shot today. It just confirmed our belief that this is all one big scam.
The embedded tweet below should explain everything. In the event it doesn’t load, here is a direct link to the tweet: BMTC’s ITS Today.
BMTC’s ITS today:
Look at the Time Stamps.#Karnataka #Bangalore #SmartCity #Corruptionhttps://t.co/ve36gxTNIZ pic.twitter.com/xaL3IiT31x— BESTpedia (@BESTpedia) August 19, 2016
![]()